Vitamin D Intake ... Regular Sunlight Exposure

"Vitamin D is made in the skin when it’s exposed to sunlight. Sun exposure is by far the best way to boost vitamin D levels, particularly because very few foods contain significant amounts.""Midday, especially during summer, is the best time to get sunlight.""At noon, the sun is at its highest point, and its UVB rays are most intense. That means you need less time in the sun to make sufficient vitamin D.""Many studies also show that the body is most efficient at making vitamin D at noon.""For example, in the UK, 13 minutes of midday sunlight exposure during summer three times per week is enough to maintain healthy levels among Caucasian adults.""Another study found that 30 minutes of midday summer sun exposure in Oslo, Norway was equivalent to consuming 10,000–20,000 IU of vitamin D,""The commonly recommended daily dose of vitamin D is 600 IU (15 mcg).""Not only is getting vitamin D around midday more efficient, but it might also be safer than getting sun later in the day. One study found that afternoon sun exposure may increase the risk of dangerous skin cancers."healthline
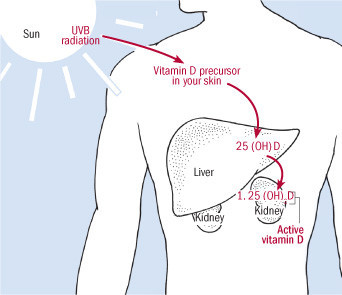 |
| The sun's energy turns a chemical in your skin into vitamin D3, which is carried to your liver and then your kidneys to transform it to active vitamin D. Harvard Health Publishing |
There is a link between sunlight and serotonin levels,the hormone that makes us feel good. The lack of sunlight can make some people susceptible to developing seasonal affective disorder when shorter fall days appear and winter brings us fewer daylight hours. An Australian study found that people had higher levels of serotonin in bright sunny days than on cloudy days. The increased levels of the hormone lead to greater feelings of calm and satisfaction, with lower levels of depression and anxiety.
Researchers speculate that the way UV light forces melanocytes, cells producing dark pigment in skin to release endorphins may explain the link between sun exposure and increased serotonin. Melatonin, the hormone that helps regulate the body's sleep-wake cycle, is encouraged in production through regular sunlight exposure. Melatonin helps as well to regulate our circadian rhythm, the body's internal clock that signals when to be alert and when to rest.
Our amygdala, the emotional part of the brain, is significantly more reactive following a bad night's sleep, leaving us likely to feel cranky. Exposure to sunlight can encourage feelings of drowsiness, so we can drift to sleep more readily, leading to a more comfortable daytime experience emotionally. Simply put; time spent in the sun has the potential to allow us to sleep soundly.
Just one hour in the sun, according to research undertaken at Medical University of Graz in Austria, can boost a man's testosterone levels by 69 percent, helping to balance mood, sex drive and cognitive function, all achieved through vitamin D, produced following sunlight exposure. A link was identified between low levels of vitamin D and low levels of the female sex hormone estrogen, by researchers in China who studied the effect on post-menopausal women.
Vitamin D has a critical role in helping the body to absorb calcium, responsible for bone strengthening. Lack of vitamin D has been associated with osteoporosis, rickets and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Rates of falls in elderly people were found in a review by the Cochrane Library, due to the effects of brittle bones, that could be reduced by over a quarter if the elderly were prescribed supplements of vitamin D.
 |
Casual exposure to sunlight is responsible for 90 percent of a person's vitamin D requirements; the best source of the nutrient. Experts believe on average that people should aim for 10 to 30 minutes of midday sunlight, several times weekly. A dose of vitamin D could also improve intellect. Scientists from the University of Manchester found higher levels of vitamin D linked with improved mental ability in middle-aged and older men.
In their study, men were tested for memory and speed recollection, along with mood and physical activity levels before blood samples were taken. Men with higher levels of vitamin D consistently outperformed those with lower levels. Even on a cloudy overcast day we are exposed to 10,000 lux (light is measured in a unit called lux) in comparison with 500 lux, spending time indoors.
Labels: Circadian rhythm, Melatonin, Seasonal Affective Disorder, Serotinen, Sleep, Sunlight Exposure

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home