Western Arctic Acidification
"In other [oceans], you may have a small part with low pH, but the Arctic Ocean is the first one we have observed with a larger scale acidification."
"During the summer melt time, the C02 directly goes to sea water."
"It's a short food web [in the Arctic]. When your food web is not as complex, it's more vulnerable."
"That [data] may be of value in the lower latitudes. The lower latitudes will go through that state in the future."
Wei-Jun Cal, University of Delaware
"That [depth of acidification] surprised everyone. But this builds up very, very quickly over time."
"If you have a change in circulation, plus acidification, things can happen more rapidly. These different processes may interact."
Richard Feely, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S.
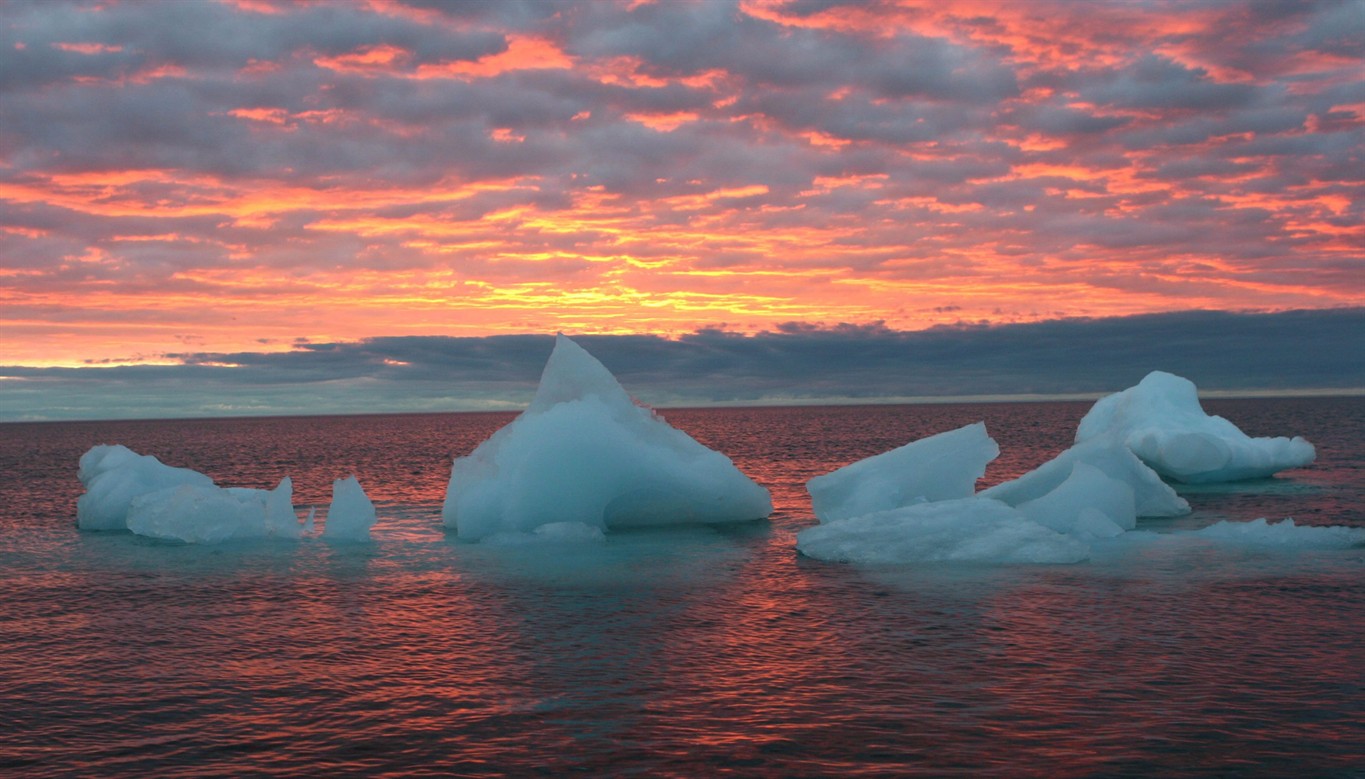 |
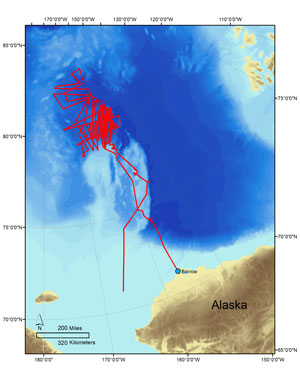
| In this Sept. 13, 2006 file photo, ice chunks float in the Arctic Ocean as the sun sets near Barrow, Alaska. Scientists have found the world's first large-scale area of acidified water in the open ocean in the seas of the western Arctic.The say the area of acidified water in the Canada Basin has expanded northwards by about 500 kilometres since the mid-90s. THE CANADIAN PRESS/AP Photo/Arctic Sounder, Beth Ipsen |
The open ocean of the western Arctic has conveyed to the enquiring minds of scientists just how much the increasing levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide is impacting on ocean acidification. And the study conclusions undertaken by Wei-Jun Cai and co-author Richard Feely, published recently in the journal Nature Climate Change, describes their journey to discovery and the conclusion of their observations and statistics. None of which are very appealing as they mapped the rate of acidification of the seas of the Canada Basin.
Through their calculations, comparing data from the mid-1990s to those up to 2010, the area of acidified water in the Canada Basin expanded northerly up to 84 degrees latitude; about 500 kilometres further north during that time frame. The acidified pool is also much deeper as it has progressed, discovered as low as 250 metres in depth representing a 100 metre increase.
The increasing levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide leads to ocean acidification and now the world's largest-scale area of such acidified open sea has been pinpointed in the western Arctic as the water becomes increasingly acidic, absorbing gas from the atmosphere making the Arctic Ocean the swiftest acidifying body of water than any ocean elsewhere on Earth. Six times what it had been twenty years ago.
The disappearance of summer sea ice due to climate change has accelerated that buildup since there is less ice cover, and the longer that a water surface is exposed to the atmosphere rich in C02, the greater the absorption of acidifying gas. As melt water sinks, picking up C02 generated from organisms on the continental shelf, the process is aided and aided again through atmospheric currents driving water from the Pacific into the Canada Basin.
Since the Pacific tends to be more acidic than the Arctic, resulting from greater exposure to the atmosphere and C02 generated by plants living in it, all these revealed interchanges aid the process. In waters outside the Arctic acidification is proven to damage young shellfish, slowing the natural development of theropods, the base of the northern food web.
Geospatial access
 Biological and Chemical Oceanography
Biological and Chemical Oceanography
Ocean Acidification in the Canada Basin: Roles of Sea Ice
Labels: Acidification, Bioscience, Climate Change, Environment

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home