Help Yourself Avoid Chronic Inflammation
"Unlike acute inflammation, which benefits health by promoting healing and recovery, chronic inflammation is characterized by persistent increases in inflammatory proteins all throughout the body and can damage health and promote several major diseases."
"People typically don't know that they have chronic inflammation until it's too late."
"Diet is one of the key factors that influences inflammation in the body. Whereas fried foods, red meat, sodas, and white bread and pastries that have refined carbohydrates tend to increase inflammation, fruits, nuts, green leafy vegetables, tomatoes and olive oil tend to reduce inflammation."
"Chronic inflammation is involved in not just a few select disorders, but a wide variety of very serious physical and mental health conditions. Indeed, chronic inflammatory diseases are the most significant cause of death in the world today, with more than 50 percent of all deaths being attributable to inflammation-related diseases."
"Chronic inflammation can also cause threat sensitivity and hyper-vigilance, which gives rise to anxiety disorders and PTSD, as well as fatigue and social-behavioural withdrawal, which are key symptoms of depression."
George Slavich, associate professor of psychiatry and biobehavioural sciences, UCLA
"The 'damage accumulation' theory is a possibility, but the reality is that we do not know whether inflammation is causing these health and functional problems, or whether it's an indication that some other process is evolving that undermines health."
"The evidence is clearer for cardiovascular disease, since it has been demonstrated that blocking inflammation with specific drugs prevents cardiovascular events. For the other outcomes, it's still uncertain."
Luigi Ferrucci, scientific director, National Institute on Aging
 |
| Scientists call for early diagnosis, prevention and treatment of inflammation to reduce risk of chronic diseases. |
Although medical researchers don't fully comprehend the mechanisms of the impact of certain behaviours' influence on chronic inflammation, a few examples are clearly recognized. Cigarette smoking and air pollution irritate the arteries which stimulates inflammation, leading to heart disease. By boosting age-related immune system deterioration (known as immunosenescence) and by promoting vascular and brain aging in combination, neural and cognitive function becomes degraded; chronic inflammation can contribute to cognitive decline and mental health disorders.

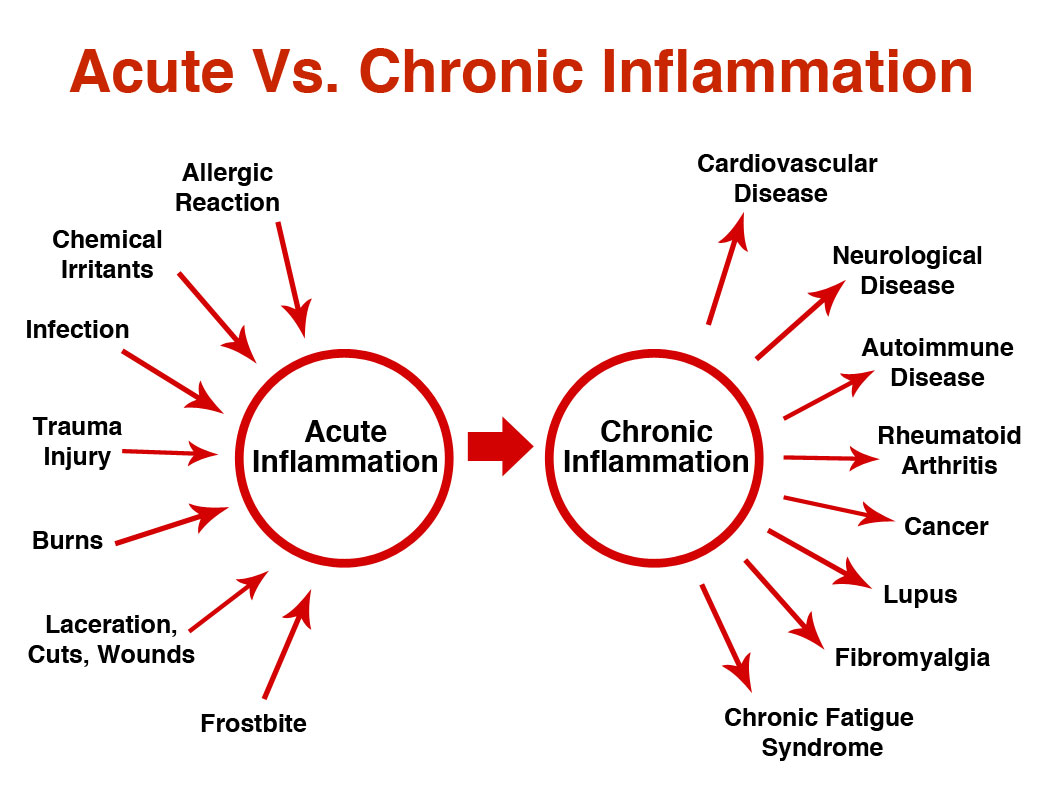
There are two types of inflammation; one of which is familiar to anyone who has sustained a wound of some kind, has had an infection or an injury like an ankle sprain; these are 'acute' inflammations where the immune system reacts to encourage healing and where, once the injury heals, the inflammation disappears. Chronic inflammation is not quite so detectable and more insidious in nature, initiating with no apparent cause ... and it never stops. The inflammatory response when the immune system is activated is not intermittent as in an injury or infection; it remains active constantly, at a low level.
Experts in the field theorize this type of inflammation may result from an infection that fails to resolve itself; an abnormal immune reaction, or lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor sleep, or exposure to environmental toxins where, over time the condition can damage DNA, ultimately leading to heart disease, cancer and other serious disorders. When an autoimmune disease like Crohn's disease, lupus or Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed, this is usually when people learn they have chronic inflammation.
 |
Chronic inflammation is held to be instrumental in the development of heart disease, cancer, kidney disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, neurodegenerative disorders, cognitive decline and mental illnesses such as depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and schizophrenia -- an entire shopping list of critical, health-destroying chronic illnesses, all attributable to chronic inflammation, according to the experts' closest-held theories.
Social isolation, psychological stress, disturbed sleep, chronic infections, physical inactivity, poor diet, obesity and exposure to air pollutants, hazardous waste products, industrial chemicals and tobacco smoke are all thought to play a part in the risk of chronic inflammation. Despite which, there is a strongly-held belief among experts that people are able to reduce this risk through changes in lifestyle which would include a healthy diet, improved sleep, regular exercise, smoking cessation and decreasing stress and exposure to pollutants.
The belief among scientists is that chronic inflammation causes oxidative stress in the body, an imbalance between dangerous free radicals production (molecules that do harm to healthy body tissue) and antioxidants (substances that clean up waste products and neutralize them). This can have the effect of damaging DNA, along with proteins and fatty tissue, in turn accelerating biological aging. In hopes of dispelling the uncertainties and arriving at more secure answers to these threats, scientists feel more research is required to identify biomarkers or other substances pointing to chronic inflammation.
 |
| Inside Out Health & Wellness |
Labels: Chronic Inflammation, Diet, Disease, Exercise, Health, Research

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home