Measuring Greenhouse Gases
"We keep burning fossil fuels. CarboTn dioxide keeps building up in the air. It's essentially as simple as that."
Ralph Keeling, Scripps scientist, Scripps Institute of Oceanography, Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii
 |
The original device used by Charles Keeling to measure atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide.
(Ted Coran)
|
"As a scientist, what concerns me the most is not that we have passed yet another round-number threshold, but what this continued rise actually means that we are continuing full speed ahead with an unprecedented experiment with our planet, the only home we have."
Katharine Hayhoe, climate scientist, Texas Tech University
"As far as we can tell, the Earth hasn’t experienced that in the last 420 million years. How the Earth will respond, there is no precedent in the geological record."
Gavin Foster, lead author, study, professor of isotope geochemistry, University of Southampton, Britain
"Due to nuclear reactions in stars, like our sun, over time they become brighter [contributing to global warming]."
"This means that, although carbon dioxide concentrations were high hundreds of millions of years ago, the net warming effect of CO2 and sunlight was less."
"It’s a level of forcing [spike in C02] that has not been experienced by the Earth, as far as we can tell. It puts the enormity of what we’re doing in context."
Dan Lunt, study co-author, professor of climate science, University of Bristol, Britain
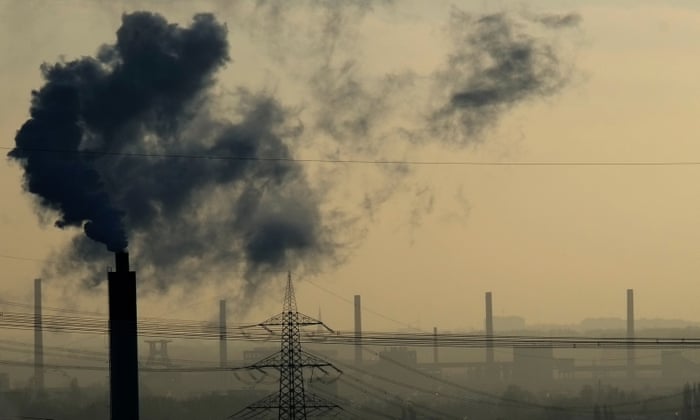 |
Smoke rises from a power plant in Bottrop, western Germany.
Photograph: Patrik Stollarz/AFP/Getty Images
|
The conclusion researchers came to was that atmospheric C02 will top 410 ppm for 2018. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration last month revealed the alarming fact that global carbon emissions have been measured and found to be at an all-time high. Measurements at the Mauna Loa Baseline Atmospheric Observatory in Hawaii registered 405.1 ppm in 2017, representing an increase of 3 ppm. The past five years of C02 increases sees an unprecedented growth rate.
 |
Looking to the future, by 2300 it appears likely the Earth will have been transformed, resulting from the endless C02 rising into the atmosphere through fossil fuel consumption, meaning the globe may hit a level not seen in 420 million years in a few centuries' time, according to the study's findings. The stunning result of the research validating a galloping rate of C02 production is taking place, doubly sounds the environmental alarm for the future.
While carbon dioxide levels fluctuated over the millennia, it had never before exceeded 300 parts per million. Ralph Keeling as well as his father Charles David Keeling before him, have been responsible for keeping tabs on carbon dioxide measurements in Hawaii at the Mauna Loa Observatory since 1958. The month of April saw the average concentration in the atmosphere hitting 410.31 ppm, according to the Keeling Curve measurement series.
Never before had the record of a monthly average exceeded 410 ppm in the history of Mauna Loa record, representing a 30 percent increase in C02 in the global atmosphere. Carbon dioxide's function as a greenhouse gas reflects its capacity to trap solar radiation and confine it to the atmosphere, as the most common among all greenhouse gases produced by the burning of fossil fuels.
The measured increase in gases like carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide fuels climate change to make "the planet more dangerous and inhospitable for future generations", according to the World Meteorological Organization. Natural variability cannot explain the rise of the Earth's temperature over the past century.
Labels: Environment, Global Warming, Nature, Research

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home